4 Technologies Disrupting the Future of FinTech Industry
– Yeshwanth, Kavya, Gayatri
Getting Started:
FinTechs are proving to be a way to future-proofing banks and financial institutions to create a more financially inclusive world.
Taking the world by surprise, the fintech industry was one of the few to witness growth when the globe crumbled with COVID-19 in 2020. Read on to know the backstory.
The never-ending social distancing norms during the pandemic pushed the need for digital payments. According to Telecom TV, during the start of the pandemic, the usage of digital wallets scaled to 83% and saw 779 billion digital transactions, making cashless payment the most common method by 2022. Fintech took advantage of this opportunity and embarked on a journey to thrive.
Data shows there are a lot of potential innovations gearing up to drop in this industry in the years to come. Read on to learn more.
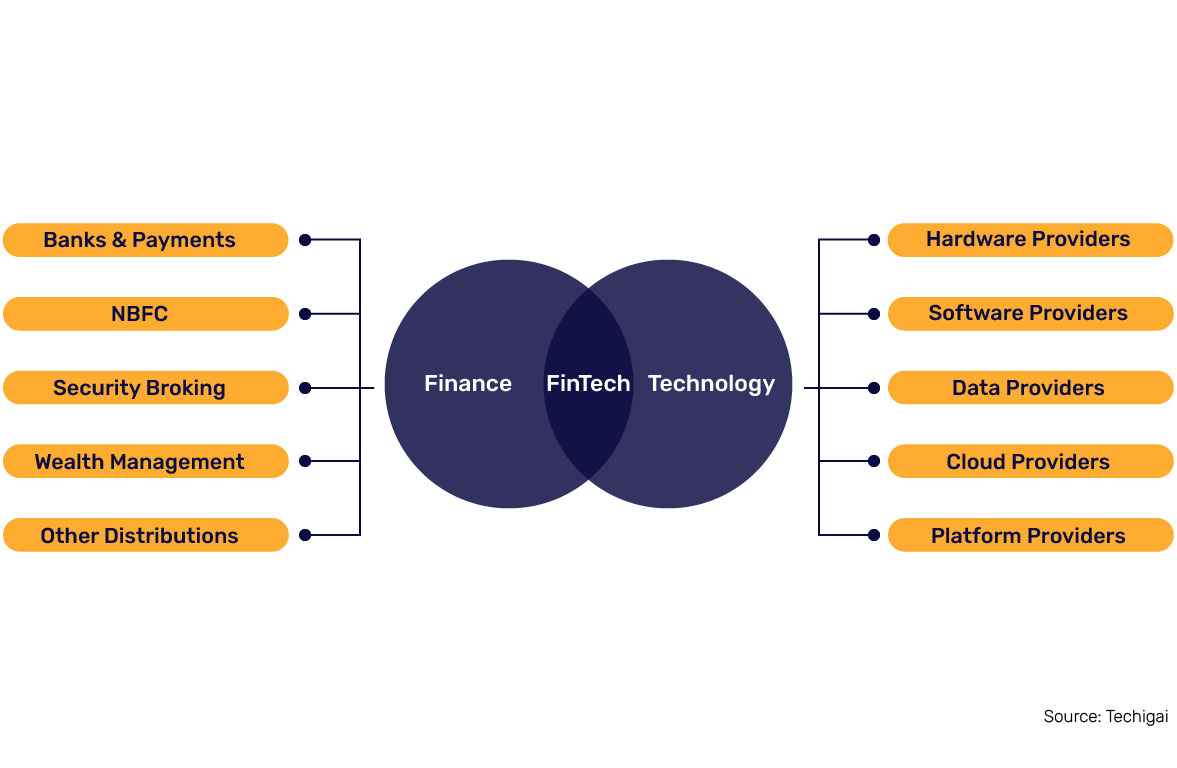
4 Technological Trends: The Plausible Future of Fintech
With the sector’s future seeming visibly bright, fintech companies will focus on branding themselves as data organizations, and rightly so.
Banks are beginning to appreciate the potential of seamless digital engagement. As per a survey of 2021, more than 50% of banking executives admitted that digital-only subsidiaries make collaboration faster and easier. So, adapting to the fast-digitalizing world and technologies is the gateway to the future of the fintech industry. How valuable is fintech innovation? Let’s first delve into the technologies used in the fintech sector to comprehend better.
1. Artificial Intelligence – For Driving Huge Value Creation
According to Mckinsey’s findings, AI alone can help the global banking industry generate up to $1 trillion additional value in a year.
In the next ten years, institutions shall leverage AI for assistance in identifying patterns across financial networks and will hone financial modeling across the sector.
A new form of decentralized machine learning, called federated machine learning , will address privacy risks associated with centralizing datasets. Advanced encryption, zero-knowledge proofs, and other secure data analysis tools will open a new dimension in consumer protection.
Furthermore, AI will penetrate the entire financial operations, including the front, middle and back offices. Intelligent chatbots, Robo advisors, market trackers, face recognition authorization, and natural language processing for fraud detection will boom.
Banking industry leaders are entirely transforming their operations by deploying AI throughout their operational lifecycle. This AI-first mindset will lead to greater operational efficiency with advanced diagnostics and automation of human tasks.
2. Cloud Computing – For Liberating Financial Service Players
Cloud computing is reforming the relationship between financial companies and customers by launching new formats like banking-as-a-service and open banking.
Before going any further, financial newbies must be aware of three forms of ‘cloud’: public, hybrid, and private cloud.
- Public: Cloud service providers own the infrastructure and sell it to organizations or the public.
- Private: Only exclusive customers own the infrastructure, which is deployable in the company’s data centers.
- Hybrid:Cloud infrastructure is maintained independently but will connect through proprietary technology.
Both fintech startups and financial organizations are racing to provide end-users with speed and reliability in their digital products and services. So, most financial organizations are going agile and realizing the benefits of moving their infrastructure to the cloud. Not just this, according to an IDG cloud computing study, more than 55% of companies are leveraging multiple public clouds.
Future of Cloud Computing For Financial Services:
- Cloud will enhance front-end sales and customer-facing environments through self-service functionality in the coming future.
- Public cloud providers are starting to encourage container technology on the cloud as it allows multiple workloads to run on a single OS. The container as a Service (CaaS) prevents overheads and enhances efficiency.
- Large scale application of big data analytics will cause a surge in cloud computing to allow resource adjustment according to the shifting demands.
- Banks will see the potential of cloud-based microservice architecture where APIs can enable machine-to-machine communication. The cherry on the cake here will be the non-requirement of enlarging the coding base to allow services to scale independently.
3. Internet of Things (IoT) – For Driving a New Era of Trust
According to Market Insights, the global IoT in the fintech industry will surge at a CAGR of 55% from 2019 to 2027.
Here’s a glimpse into the usefulness of IoT in fintech:
- It can remove redundancies in daily operations by bringing down the need for manual labor.
- In banking, IoT can solve issues of appraisal sheets, saving and spending patterns, and financial planning.
- IoT ensures robust data protection with authentications.
- It can level up risk management by fetching real-time data on consumer capital.
Allow us to take real-time scenarios of two IoT fintech startups, Stripe and Armis, to explain the prevalence of IoT in fintech. Stripe has dedicated IoT software to customize companies’ payments of all sizes through a reliable cloud-based infrastructure. On the other hand, Armis offers IoT security services to banks and financial companies, and it specializes in the automatic identification of unmanaged devices and agentless tracking.
The future of IoT in the fintech industry looks bright in these aspects:
- Social and environmental factors govern many investment strategies. For example, many countries have a target to be carbon-free. To succeed, effective monitoring of industrial energy is necessary, where IoT apps fit perfectly.
- Insurance companies will use IoT to accurately determine risks while enhancing customer engagement and simplifying the claims processes.
For instance, automotive insurers once relied on a driver’s age, address, and worthiness. With IoT, data on driver behavior like car speed and frequency of use at night have become the determining factors. - In banking, IoT-based property financing with the integration of IoT and blockchain shall refine risk management by matching accounts with real-world transactions, thereby facilitating trust.
- Embedding banking services to wearables (digital payments, for instance) is one arena where IoT can bring customers and banks closer.
4. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) – For Streamlining Digital Tasks
RPA in the financial services market, whose value was at $345 million in 2020, will reach $4880 million by 2030, according to Allied Market Research.
Are you wondering about the possible reasons for such a considerable imminent surge? Compared to all other technologies disrupting the fintech sector, RPA is one step ahead as it already works across financial institutions’ back and middle office operations. A few benefits of RPA for banking are that it helps automate accounting, accounts payable and receivable, financial reporting and treasury processes, and labor hour reviews and adjustments.
RPA providers are exploring new verticals in financial services to breakthrough. In the future, we can expect RPA to be powerfully integrated with AI, thereby improving its effectiveness in dealing with complex business cases.
Although RPA’s function is to automate repetitive tasks, we expect it to penetrate the fintech industry more deeply, where bots can be the primary decision-makers. Given the right conditions, we can also see the shift from a company-centric approach to a customer-centric approach, with RPA making interfaces seamless to customers.
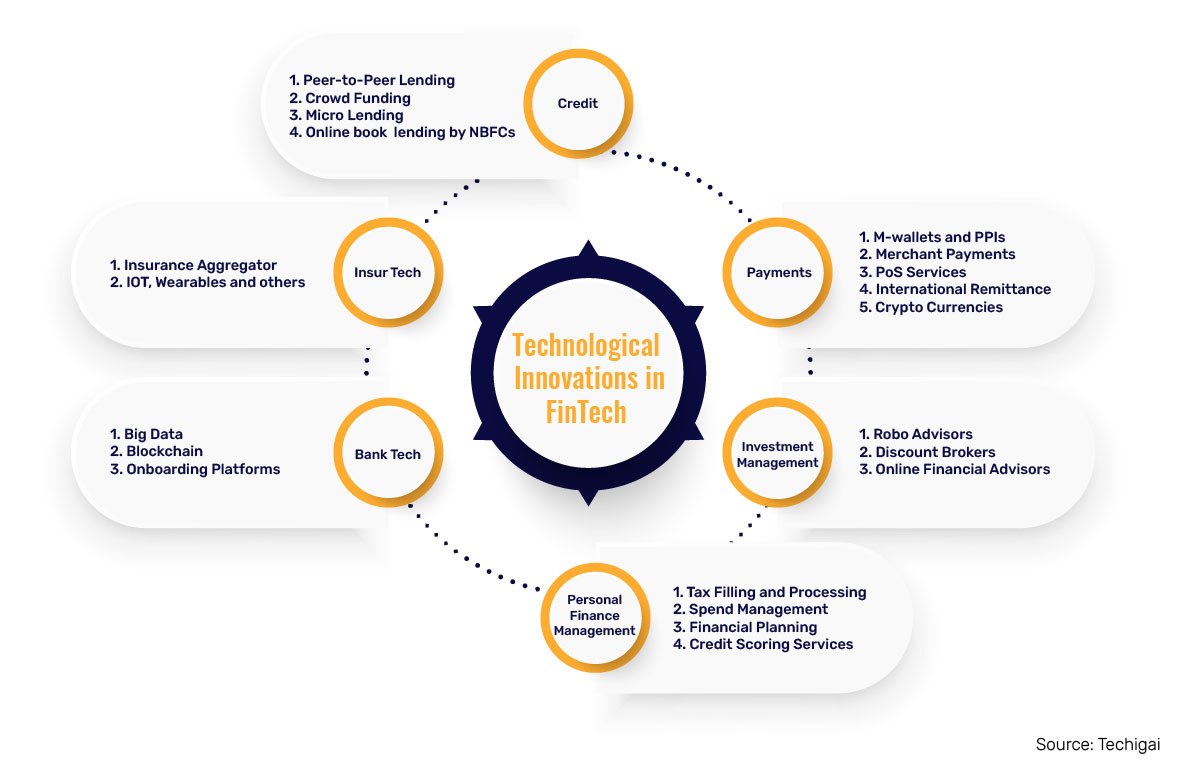
Emerging Areas of Technological Innovations in FinTech
Final Thoughts
As days pass, we will see a new generation basking in the perks of the fintech revolution and banking becoming a non-physical client experience.
Traditional banks and financial institutions have always viewed technology as an enabler to business proposals instead of creating new propositions.
However, fintech companies are changing that role by leveraging digital technologies to create new business propositions and targeting new market segments to improve their reach, customer service, and operational effectiveness with the ever-evolving market and technological advances.
“
Banking has to work when and where you need it. The best advice and the best service in the financial services happens real time.
Brett King




